Narrow Houses
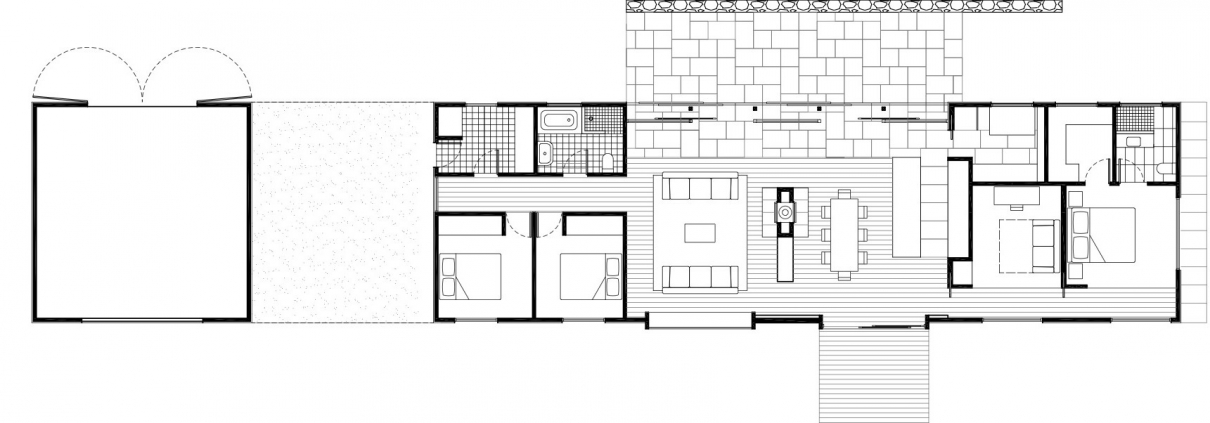
The design of narrow dwellings has been the subject of my research for several decades. The term narrow-front is typically used to describe dwellings whose street-facing exteriors measure 25 feet (6 meters) or less; they can be constructed in a detached, semidetached, or attached form. Also known as terraced homes, townhouses, or shotgun dwellings, they have been constructed throughout history on several continents and have maintained their appeal by offering privacy and green yards, even in compact configurations. Built in high densities, they help:
- halt urban sprawl;
- reduce the amount of construction material;
- and improve energy efficiency once occupied.
Recent societal changes have brought about renewed interest in narrow houses among architects, town planners, and housing officials. This building type, which dates back two millenia, offers relevant solutions to contemporary challenges. Chief among them is the need to adopt sustainable approaches to the planning of neighborhoods and houses.
The desire to reduce the footprint of a house on a site endowed with natural features was the primary motive behind many of the projects featured in narrow house designs. Other objectives included the need to minimize building costs, accommodate a number of functions in a relatively small space, fill in an urban gap, or simply conceive of a sculptural dwelling.
These constraints led to innovative thinking and intriguing designs. Locating and bringing light and views to all rooms, including the house’s service core, was another concern. In keeping with current environmental challenges, the architects considered orientation for passive solar gain and minimal disruption to the landscape.
Narrow Houses New Directions in Efficient Design By Avi Friedman


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!